WAF vs. ACLs vs. Security Groups: Safeguarding Your Cloud Resources
As businesses increasingly embrace cloud computing, ensuring the security of cloud resources becomes paramount. In the realm of cloud security, three critical tools stand out: Web Application Firewalls (WAFs), Access Control Lists (ACLs), and Security Groups. In this article, we will explore the differences, use cases, and benefits of each, empowering you to make informed decisions on how to effectively protect your valuable cloud assets.
Understanding Web Application Firewalls (WAFs)
Web Application Firewalls are designed specifically to protect web applications from a wide range of cyber threats. WAFs analyze incoming and outgoing HTTP/HTTPS traffic and apply security policies to identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities and attacks. With customizable rule sets, WAFs provide granular control over web application traffic, helping prevent common threats such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks.
One of the other biggest differences between ACL and a WAF is that a WAF sits in front of your load balancer/CDN, whereas an ACL sits behind your load balancer/CDN, right at the subnet level. A WAF mitigates attacks before they reach your application. This is easiest to see in a diagram:
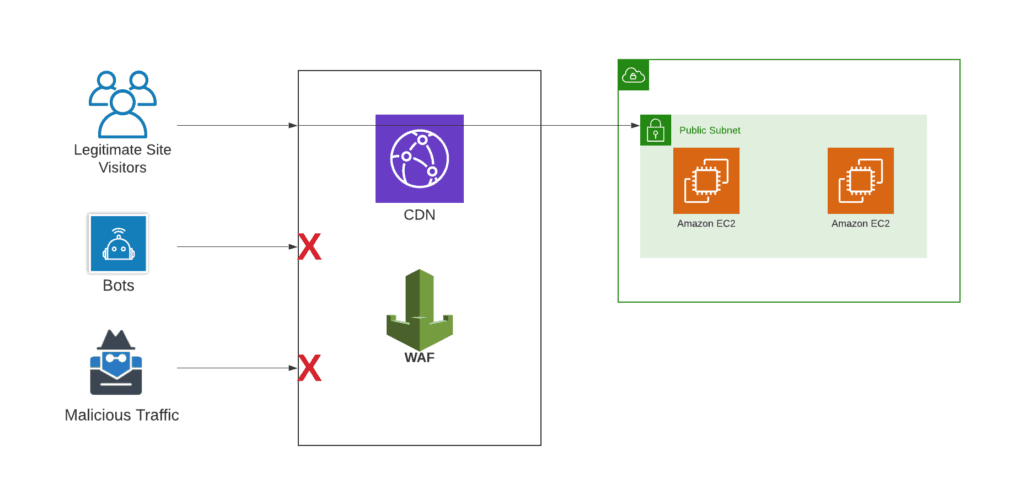
Exploring Access Control Lists (ACLs)
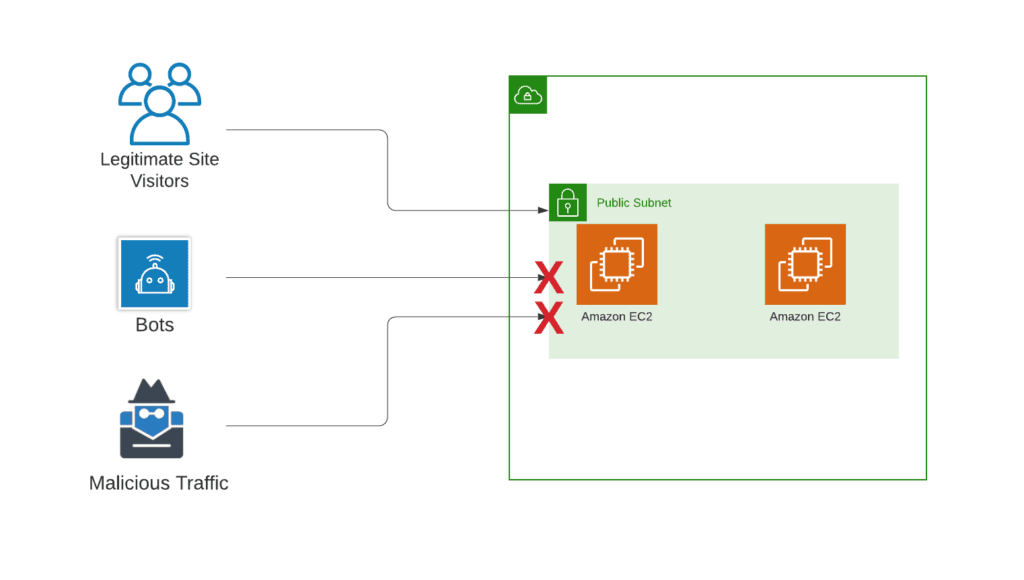
Access Control Lists serve as network-level filters that determine which network traffic is allowed or denied based on defined rules. ACLs operate at the subnet level and are commonly used in infrastructure-level security. By permitting or blocking specific IP addresses or IP ranges, ACLs help control inbound and outbound traffic flow. They are often employed to protect network resources from unauthorized access and limit communication between different subnets or security zones.
Network ACLs configured to block common bot/malicious traffic IPs:
Unveiling Security Groups
Security Groups, on the other hand, operate at the instance level within a cloud environment. They act as virtual firewalls, controlling inbound and outbound traffic for individual instances or groups of instances. With security groups, you can define rules that allow or deny specific protocols, ports, or IP ranges. They provide a highly flexible and scalable approach to securing cloud resources, enabling you to create fine-grained access controls based on instance-level requirements.
Use Cases and Benefits
4.1 WAFs:
- Protection against web application vulnerabilities and attacks, ensuring application availability and integrity.
- Safeguarding sensitive data by preventing unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Compliance with industry regulations and standards, such as PCI DSS or HIPAA.
- Enhanced visibility and reporting capabilities to identify potential threats and track application security.
4.2 ACLs:
- Enforcing network-level security by controlling traffic between subnets and security zones.
- Protection against unauthorized access to critical infrastructure resources.
- Segmentation and isolation of network segments for improved security and reduced attack surface.
- Defense against network-level threats like IP spoofing or reconnaissance attacks.
4.3 Security Groups:
- Instance-level security controls, allowing fine-grained access management for cloud resources.
- Scalable and flexible approach to managing access permissions for individual instances or groups of instances.
- Integration with other cloud services, such as load balancers or autoscaling groups, to maintain security during resource scaling.
- Easy management and maintenance, with the ability to update rules dynamically as per evolving security requirements.
Conclusion
Securing your cloud resources is a critical aspect of maintaining a robust and resilient infrastructure. Understanding the differences and benefits of Web Application Firewalls (WAFs), Access Control Lists (ACLs), and Security Groups allows you to implement a comprehensive security strategy tailored to your specific needs. By leveraging the right tools and employing best practices, you can protect your valuable assets from a wide range of threats and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of your cloud-based applications and data.
Remember, effective cloud security involves a multi-layered approach, combining these tools with other security measures such as encryption, strong authentication, and regular security assessments. Stay proactive, stay vigilant, and keep abreast of the evolving threat landscape to safeguard your cloud resources effectively.


